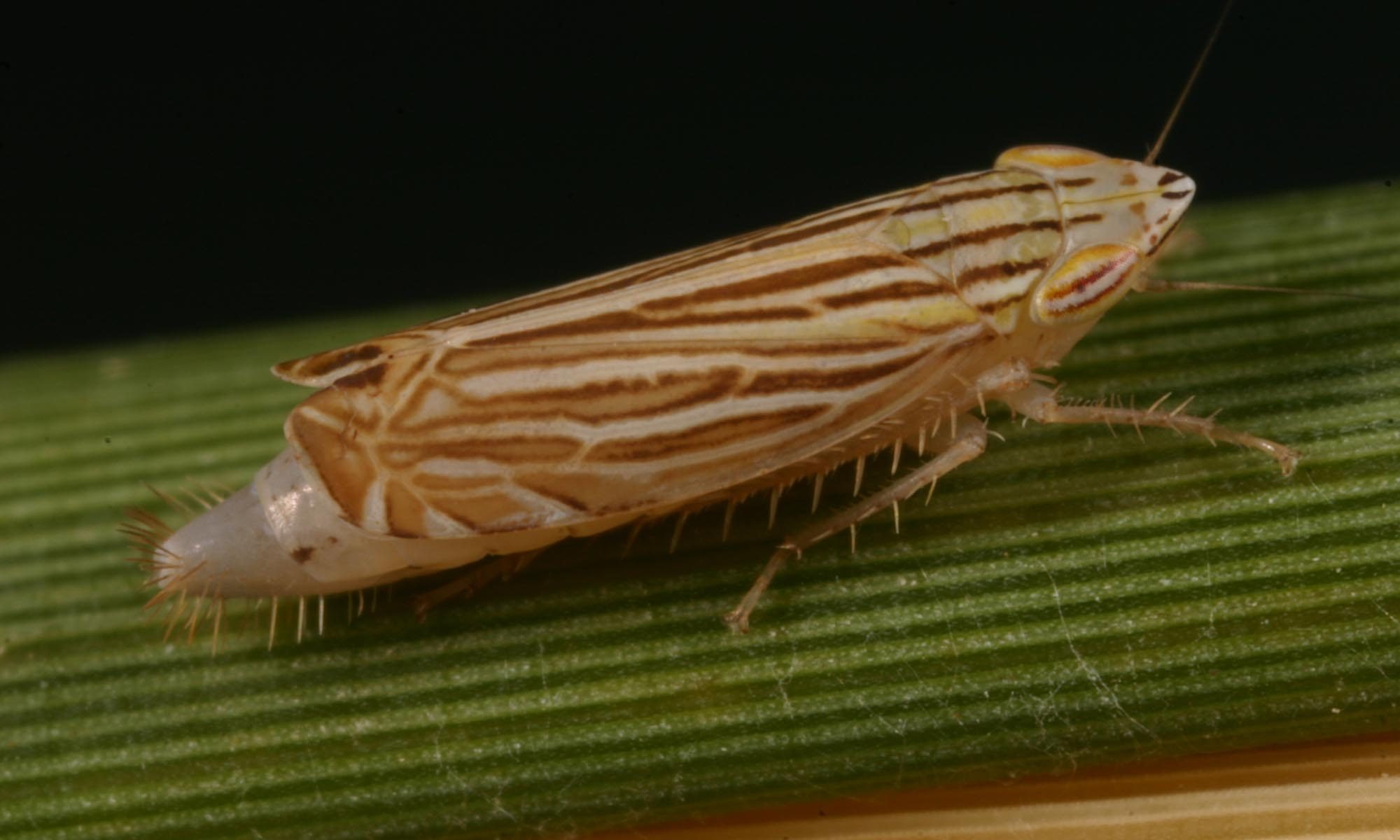
by C. H. Dietrich, Center for Biodiversity, Illinois Natural History Survey, Sept. 20, 2000; Revised Feb. 13, 2006
Note: Classification follows Oman et al. 1990 except Mileewinae, Evacanthinae, and Errhomeninae are treated as subfamilies separate from Cicadellinae, following Young (1968 and 1986).
Scale bars are 1 mm
Acostemminae

Range: East Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka.
Known diversity: 7 genera, 20 species.
Ecology: Unknown; inhabiting forests.
Diagnosis: Medium to large leafhoppers; head weakly produced with transverse carina between ocelli, ocelli on anterior margin of crown near eyes, antennal ledge weak or absent; forewing venation complete, usually with supranumerary crossveins; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1; male valve fused to pygofer, plates at least partially fused medially.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae.
Adelungiinae
[Reduced to tribal status within Megophthalminae by Dietrich, C. H. 2005. Florida Entomol. 88:502-517]

Range: Eremian (Africa, southern Europe, Middle East).
Known diversity: 13 genera, 60 species.
Ecology: On desert shrubs.
Diagnosis: Small, cylindrical leafhoppers; ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures absent, clypellar suture incomplete; forewing with numerous supranumerary crossveins; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1 or 2+0.
Similar to: Agalliinae
Agalliinae
[Reduced to tribal status within Megophthalminae by Dietrich, C. H. 2005. Florida Entomol. 88:502-517]

Range: Worldwide, most diverse in Neotropics.
Known diversity: 37 genera, 600 species.
Ecology: On herbs, shrubs, or trees.
Diagnosis: Small, cylindrical leafhoppers; ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures absent; forewing with few or no supranumerary crossveins; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1 or 2+0.
Similar to: Adelungiinae, Megophthalminae, Evansiolinae.
Aphrodinae

Range: Mostly Holarctic, sparsely distributed in Africa and SE Asia.
Known diversity: 8 genera, 20 species.
Ecology: On herbs and grasses, often feeding on or near the roots.
Diagnosis: Medium sized, depressed leafhoppers; head produced, ocelli on crown near margin, distant from eyes, eye emarginate mesially; forewing venation complete, hind wing marginal vein often incomplete; hind femur macrosetal formula various, often 2+2+1; male plates ligulate.
Similar to: Xestocephalinae, Deltocephalinae.
Arrugadinae

Range: Tropical South America.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 3 species.
Ecology: Unknown.
Diagnosis: Medium sized, cylindrical leafhoppers; head produced with upturned apex, ocelli on margin of crown distant from eyes; wing venation complete; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+2+1; male plates triangular.
Similar to: Aphrodinae, Deltocephalinae (Arrugadini should probably be included in this subfamily as a tribe).
Austroagalloidinae

Range: Australia.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 10 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Medium sized, cylindrical leafhoppers; head short, rounded, with distinct dorsal shelf, ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures complete; forewing crossvein s absent; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+0.
Similar to: Eurymelinae, Idiocerinae.
Bythoniinae
(Bythonia Oman was placed in Iassinae by Blocker and Webb (1990, Ent. News 101: 293-296), but this placement was not accepted by Nielson and Knight (2000, Rev. Bras. Ent. 17: 81-156).

Range: South America.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 5 species.
Ecology: On trees in rainforests.
Diagnosis: Medium sized, dark reddish brown leafhoppers; crown short, margin carinate, ocelli on margin of crown distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures and epistomal suture complete; forewing membrane setose, venation complete, hind wing veins R3+4 and M1+2 free; hind femur macrosetal formula variable, usually 2+2+1; male plates slender, ligulate; female second valvulae without widely spaced dorsal teeth.
Similar to: Iassinae
Cicadellinae

Range: Worldwide, poorly represented in Palearctic and Australia.
Known diversity: 350 genera, 3100 species.
Ecology: Various; usually on herbs and grasses in moist areas.
Diagnosis: Medium to large cylindrical leafhoppers; head produced, face strongly inflated, ocelli on crown distant from anterior margin, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; forewing venation complete, inner apical cell elongate with base narrow and inner corner usually basad of outer corner; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+1 or 2+1+1; male plates usually triangular or parallel sided, not ligulate.
Similar to: Errhomeninae, Evacanthinae.
Coelidiinae

Range: Worldwide except Europe.
Known diversity: 126 genera, 1300 species.
Ecology: Various; usually on trees and shrubs in forests.
Diagnosis: Medium to large cylindrical leafhoppers; head with crown narrow, ocelli on or near anterior margin of crown, distal segment of rostrum cylindrical and much longer than penultimate segment; forewing usually without crossvein r-m1; front tibia with accessory row of macrosetae in basal half adjacent to row AV; hind femur usually with macrosetal formula 2+2+1 with penultimate pair widely separated; tibia with basal seta of AD offset; ovipositor slender with median dorsal tooth; aedeagus usually linear.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae, Tartessinae.
Deltocephalinae
(the concept of this subfamily was recently expanded to include Eupelicinae, Koebeliinae, Paraboloponinae, Penthimiinae, and Selenocephalinae; see Dietrich, C. H., and R. A. Rakitov. 2002. J. New York Entomol. Soc. 110: 1-48, and Dietrich, C. H., and D. A. Dmitriev. 2003. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer. 96: 766-775)

Range: Worldwide.
Known diversity: 750 genera, 6500 species.
Ecology: Various; abundant in grasslands and savannas.
Diagnosis: Small to medium-sized leafhoppers; head with ocelli on margin of crown near eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli, antennal ledges reduced or absent; forewing usually with one or more crossveins in clavus; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1 with penultimate pair close-set; male valve and plates usually triangular.
Similar to: Acostemminae, Aphrodinae, Arrugadinae, Drakensbergeninae, Eupelicinae, Koebeliinae, Neobalinae, Selenocephalinae, Stegelytrinae, Xestocephalinae.
Drakensbergeninae

Range: South Africa.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 2 species.
Ecology: On grasses.
Diagnosis: Small, pale, brachypterous leafhoppers; head produced, ocelli on crown near margin; lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli, frontoclypeus inflated and extended onto crown laterally; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1+1 or 2+1; male genitalia as in Deltocephalinae.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae (Doraturini), Euacanthellinae.
Errhomeninae

Range: northern Palearctic, northwestern Nearctic.
Known diversity: 10 genera, 70 species.
Ecology: On herbs and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large, robust, usually mottled brown leafhoppers, female often brachypterous; head with ocelli on crown, lateral frontal sutures not extended to ocelli, antennal ledge transverse, frontoclypeus usually inflated; forewing with inner apical cell short and oblique; middle femur usually with AM1 developed; hind femur with three or more pairs of dorsal macrosetae; male plates ligulate.
Similar to: Cicadellinae, Aphrodinae.
Euacanthellinae

Range: Australia, New Zealand
Known diversity: 1 gen, 2 species.
Ecology: On grasses.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized brown leafhoppers with sexually dimorphic wings; head produced, ocelli on crown near margin, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli, frontoclypeus inflated, gena acutely emarginate below eye, eye with mesial margin entire; metathoracic femur macrosetal formula 2+1; male plates ligulate.
Similar to: Aphrodinae, Drakensburgeninae.
Eupelicinae
[Treated as junior synonym of Deltocephalinae by Dietrich, C. H., and R. A. Rakitov. 2002. J. New York Entomol. Soc. 110: 1-48]

Range: Worldwide except Neotropical.
Known diversity: 10 genera, 100 species.
Ecology: On herbs and grasses.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large leafhoppers, often extremely elongated and seedlike; head strongly produced, often spatulate, ocelli on crown near margin; wings often sexually dimorphic, forewing veins raised, membrane shagreen; hind femur with macrosetal formula 2+1 or 2+0.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae (Hecalini), Aphrodinae.
Eurymelinae

Range: Australia, New Guinea.
Known diversity: 33 genera, 120 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs, especially Eucalyptus; often gregarious, ant-attended. Diagnosis: Large, robust leafhoppers, often brightly colored; head short, ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; forewings macropterous, usually with supranumerary R branches but without well delimited Rs (s crossvein absent), r-m1 elongate; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+0; female second valvulae broad with large dorsal teeth.
Similar to: Idiocerinae, Macropsinae.
Evacanthinae
(=Nirvaninae, see Dietrich, C.H. 2004. Syst. Entomol. 29: 455-487)

Range: Palearctic, Oriental, Nearctic.
Known diversity: 14 genera, 100 species.
Ecology: On undergrowth in moist forests.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, cylindrical leafhoppers; head produced, crown usually with oblique striations and with a well developed submarginal carina, ocelli on crown near margin, frontoclypeus with medial carina; forewing macropterous (submacropterous in type genus), R two branched, r-m1 absent.
Similar to: Cicadellinae, Nirvaninae, Signoretiinae, Typhlocybinae.
Evansiolinae

Range: Juan Fernandez Islands (Chile)
Known diversity: 1 genus, 3 species.
Ecology: Unknown.
Diagnosis: Small brown leafhoppers with brachypterous to submacropterous wings; head produced, crown depressed, ocelli absent; forewing venation reticulate; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+0 or 2+1, tibia row AV with macrosetae restricted to distal half; male valve broadly fused to pygofer.
Similar to: Agalliinae, Ulopinae.
Hylicinae

Range: tropical Africa and Asia
Known diversity: 14 genera, 40 species.
Ecology: In forests on trees.
Diagnosis: Large, robust, usually dark brown leafhoppers, dorsal parts of body and forewings clothed with setae or scales, often with bizarre head process and projections on thorax; head usually strongly produced, ocelli on crown, frontoclypeus inflated, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; forewing crossvein m-cu2 apparently connected to CuA; abdomen depressed with lateral margins sharp.
Similar to: Cicadellinae, Coelidiinae.
Iassinae

Range: Worldwide
Known diversity: 50 genera, 700 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, usually green or brown leafhoppers; head with ocelli distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures not extended to ocelli; forewing macropterous, often setose; hind wing veins R4+5 and M1+2 usually confluent; male with sternum VIII enlarged and largely concealing plates, plates ligulate; female second valvulae usually with 2-3 widely spaced dorsal teeth.
Similar to: Scarinae (sometimes treated as a tribe of Iassinae), Ledrinae.
Idiocerinae

Range: Worldwide
Known diversity: 90 genera, 720 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Small to medium-sized, often brightly colored leafhoppers; head short and broad, ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures usually extended to ocelli; forewing macropterous, usually without crossvein s; hind wing venation complete; hind tibial row PV usually with alternating long, baloonlike and short, simle macrosetae; male valve united with pygofer; female second valvulae usually broad with numerous large dorsal teeth.
Similar to: Eurymelinae, Macropsinae.
Koebeliinae
[Reduced to tribal status within Deltocephalinae by Dietrich, C. H., and D. A. Dmitriev. 2003. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer. 96: 766-775]

Range: western North America.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 5 species.
Ecology: On Pinus.
Diagnosis: Medium sized, mottled grey or brown leafhoppers; head spatulate, ocelli on face near upper margin, distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; clypellus very narrow and tapered, extended beyond ventral genal margin. Forewing macropterous with claval crossvein, veins pustulate; hind tarsomere I with longitudinal row of platellae; male valve and plates triangular.
Similar to: Eupelicinae, Deltocephalinae (Grypotini).
Ledrinae

Range: Worldwide.
Known diversity: 70 genera, 450 species.
Ecology: Usually on trees and shrubs (Xerophloeini on grasses).
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large brown or green leafhoppers; head usually strongly produced, often spatulate, ocelli on crown distant from margin (or, in Stenocotini, in marginal grooves), lateral frontal sutures partially or completely obsolete; forewing macropterous, often with supranumerary veins; hind femur with three short stout macrosetae apically, distal macrosetae of tibial row AD with spinelike bases; male plates ligulate, partially retracted into enlarged sternum VIII.
Similar to: Scarinae, Iassinae.
Macropsinae

Range: Worldwide.
Known diversity: 26 genera, 550 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Small to medium-sized leafhoppers; head short, usually strongly punctate, ocelli on face distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures reduced or absent, gena narrow; pronotum strongly produced, clypellus produced beyond genal margin; forewing macropterous, hind wing R2+3 absent; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1 or 2+1+1; female ovipositor elongate and narrow.
Similar to: Idiocerinae, Nioniinae, Agalliinae.
Makilingiinae

Range: Philippines.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 25 species.
Ecology: Unknown
Diagnosis: Medium sized, cylindrical leafhoppers, usually black with pale markings and distinctly punctate; head produced, ocelli on crown distant from eyes, crown with pronounced marginal carina, lateral frontal sutures extended to but not beyond crown margin, gena broad without distinct emargination, frontoclypeus inflated; wings macropterous, venation complete; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+1+1.
Similar to: Cicadellinae.
Megophthalminae

Range: Afrotropical, western Palearctic, western Nearctic, and Neotropical.
Known diversity: 7 genera, 40 species.
Ecology: In dense, low growing herbacous vegetation.
Diagnosis: Small, brown, punctate leafhoppers, often with elytralike forewings and vestigial hind wings; head with ocelli on face just dorsad of carinate frontal sutures; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+0; male genitalia very similar to those of Agalliinae; female first valvulae with maculose sculpturing.
Similar to: Agalliinae, Ulopinae.
Mileewinae

Range: Pantropical
Known diversity: 4 genera, 90 species.
Ecology: On undergrowth in moist forests.
Diagnosis: Small, delicate leafhoppers, mostly dark brown dorsally, pale ventrally; head produced, ocelli on crown distant from margin, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; forewing with R two branched, without crossvein r-m1; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1+1.
Similar to: Cicadellinae, Typhlocybinae, Tinterominae.
Mukariinae

Range: Afrotropical and Oriental.
Known diversity: 2 genera, 10 species.
Ecology: In forests, sometimes under bark or on undersides of leaves.
Diagnosis: Small, depressed, yellow or black glabrous leafhoppers; head produced, ocelli on crown near margin, lateral frontal sutures obsolete; forewing venation reduced; hind femur with macrosetal formula 2+2+1, penultimate pair close-set; male valve and plates triangular, aedeagus furcate with two gonopores.
Similar to: Penthimiinae.
Neobalinae

Range: Neotropical
Known diversity: 9 genera, 50 species.
Ecology: On trees in rainforests.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large leafhoppers, often with striking color patterns; crown short, ocelli on margin not far from eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended ventromesiad of ocelli, antennal ledges well developed, oblique; front tibia with accessory row of macrosetae between AD and AV; hind femur with two or more pairs of distal macrosetae; male plates large, triangular.
Similar to: Coelidiinae, Deltocephalinae.
Neocoelidiinae

Range: New World.
Known diversity: 18 genera, 130 species.
Ecology: Usually on trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large, pale leafhoppers; head produced, often with marginal carina, crown raised and shelflike mesiad of eyes, ocelli on or near crown margin, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli, antennal ledges well developed, oblique, clypellus usually with medial gibbosity or tubercle; forewing with crossvein r-m1 absent and hind wing with R4+5 and M1+2 confluent near apex (exception Chinaia); hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1 with penultimate pair widely separated; male plates fused to valve.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae, Nirvaninae.
Nioniinae
Range: Afrotropical, Oriental, and New World.
Known diversity: 3 genera, 12 species.
Ecology: On undergrowth in forests.
Diagnosis: Small to medium sized, punctate, shining black or dark brown leafhoppers; head short, ocelli on face, gena broad; pronotum strongly produced; forewing with Rs well developed, but crossvein s usually absent, hind wing venation complete; male plates triangular.
Similar to: Macropsinae.
Nirvaninae
[Treated as a jr. synonym of Evacanthinae by Dietrich, C. H. 2004. Syst. Entomol. 29: 455-487]

Range: Pan-tropical.
Known diversity: 40 genera, 150 species.
Ecology: On herbs and trees in tropical forests.
Diagnosis: Small to medium sized, depressed leafhoppers; head strongly produced, ocelli on crown, usually near margin, lateral frontal sutures usually not extended to ocelli; forewing vein R with branches usually reflexed, r-m1 absent; hind wing veins R4+5 often confluent preapically.
Similar to: Cicadellinae, Evacanthinae, Typhlocybinae.
Penthimiinae
[Treated synonym of Deltocephalinae; see Dietrich, C. H., and R. A. Rakitov. 2002. J. New York Entomol. Soc. 110: 1-48]

Range: Worldwide.
Known diversity: 46 genera, 245 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, depressed, ovoid leafhoppers; head produced, ocelli on crown, face usually concave in profile, lateral frontal sutures reduced; forewing apices strongly overlapping, claval crossveins present; front tibia with ablateral surface flattened and expanded; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1, often with setae crowded together on preapical process, penultimate pair close-set; male valve and plates triangular.
Similar to: Mukariinae, Iassinae.
Phereurhininae

Range: South America.
Known diversity: 3 genera, 5 species.
Ecology: Unknown.
Diagnosis: Large, depressed leafhoppers; head strongly produced, ocelli on crown distant from margin, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli, frontoclypeus inflated; pronotum with lateral carina flangelike; forewing venation complete; hind knee at rest not reaching proepimeron, macrosetal formula 2+0.
Similar to: Cicadellinae (Proconiini, probably a synonym).
Phlogisinae
[Treated as a jr. synonym of Signoretiinae by Dietrich, C. H. 2005. Florida Entomol. 88:502-517]

Range: Afrotropical and Oriental.
Known diversity: 2 genera, 2 species.
Ecology: Unknown.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, cylindrical, mostly black leafhoppers; head produced, ocelli on crown, frontoclypeus inflated, coarsely punctate; pronotum extended to scutellar suture; forewing venation complete; front femur with ventral margin bluntly angled at midlength, hind femur macrosetal formula 2+0.
Similar to: Signoretiinae.
Scarinae
(=Gyponinae) [Reduced to tribal status within Iassinae by Dietrich, C. H. 2005. Florida Entomol. 88:502-517]

Range: New World
Known diversity: 90 genera, 1300 species.
Ecology: Usually on trees and shrubs, rarely (e.g., Prairiana) on grasses.
Diagnosis: Medium to large somewhat depressed leafhoppers; head weakly to strongly produced, often spatulate, ocelli on crown distant from margin and eyes, lateral frontal sutures ending a short distance dorsad of antennal ledges; forewing venation complete, inner apical cell narrow and tapered; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1, penultimate pair close-set; male plates ligulate, strongly retracted into 8th sternum.
Similar to: Iassinae, Ledrinae.
Selenocephalinae
[Treated as jr. synonym of Deltocephalinae by Dietrich, C. H., and R. A. Rakitov. 2002. J. New York Entomol. Soc. 110: 1-48]

Range: Old World.
Known diversity: 60 genera, 330 species.
Ecology: Usually on trees and shrubs; Selenocephalus occurs on herbs in arid habitats.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, somewhat depressed leafhoppers; head weakly to moderately produced, crown depressed, margin with transverse carinae, ocelli on margin near eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended to ocelli; forewing venation complete, with one or more claval crossveins; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2+1 with penultimate pair close set; male valve and plates triangular.
Similar to: Deltocephalinae.
Signoretiinae

Range: Afrotropical and Oriental.
Known diversity: 2 genera, 25 species.
Ecology: On herbs in moist tropical habitats.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized pale cylindrical leafhoppers; head produced, crown with well developed submarginal carina, ocelli near margin of crown just laterad of carina, frontoclypeus inflated; pronotum foveate, extended to scutellar suture; forewing vein R two branched, r-m1 absent; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+0, tibia with macrosetal row PD reduced or absent.
Similar to: Evacanthinae, Phlogisinae, Typhlocybinae.
Stegelytrinae

Range: Eremian (southern Europe, N. Africa, Middle East)
Known diversity: 3 genera, 10 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs, especially Quercus, in arid habitats.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, robust, light brown leafhoppers; head weakly produced, narrower than pronotum, ocelli on margin of crown near eyes, lateral frontal sutures reaching ocelli, rostrum short; forewing venation reticulate; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+2+1, penultimate pair widely spaced, tibia with macrosetae present between rows PD and AD.
Similar to: Coelidiinae, Deltocephalinae.
Tartessinae

Range: Australian and Oriental.
Known diversity: 38 genera, 200 species.
Ecology: On trees and shrubs, especially Eucalyptus.
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to large, cylindrical leafhoppers; head weakly produced, crown short, with distinct marginal carina, ocelli just below margin, epistomal suture well-delimited, lateral frontal sutures sinuate, extended to ocelli, face usually with irregular arcuate rows of punctures dorsally, rostrum short; pronotum strongly produced; wing venation complete; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+2 with penultimate pair widely separated, tibia with cucullate intercalary setae between larger macrosetae of row AD.
Similar to: Coelidiinae.
Tinterominae
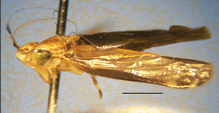
Range: Costa Rica.
Known diversity: 1 genus, 3 species.
Ecology: On undergrowth in premontane tropical forest.
Diagnosis: Small, delicate, cylindrical leafhoppers with distinctive color patterns; head produced, crown depressed, ocelli on crown distant from margin, facial sutures obsolete, antennae with pedicel greatly elongated and base of flagellum divided into 3 distinct subsegments, antennal ledges well developed, rostrum elongate; forewing vein M two branched; hind wing venation complete; hind femoral macrosetae 2+1+1, tarsi elongate.
Similar to: Mileewinae, Typhlocybinae.
Typhlocybinae

Range: Worldwide.
Known diversity: 470 genera, 5200 species.
Ecology: Various; usually arborial.
Diagnosis: Small, delicate, often brightly colored leafhoppers; head weakly to strongly produced, ocelli, if present, near anterior margin distant from eyes, gena not concealing proepisternum; forewing without crossveins basad of apical cells, R two branched; hind femur macrosetal formula usually 2+1+1, tibial row AV reduced in basal half, tarsomere I acuminate apically.
Similar to: Evacanthinae, Nirvaninae.
Ulopinae

Range: Old World.
Known diversity: 33 genera, 180 species.
Ecology: On dense, low-growing woody or herbaceous vegetation; Cephalelini on Restioniaceae.
Diagnosis: Small brown leafhoppers with elytralike forewings; head weakly to strongly produced, ocelli on crown, postfrontal sutures usually well developed; mesanepisternum with shelflike process; leg chaetotaxy greatly reduced; hind tibia usually with macrosetae absent or restricted to distal third of row AD.
Similar to: Megophthalminae, Evansiolinae.
Xestocephalinae

Range: Pantropical with sparse representation in temperate North America and eastern Palearctic.
Known diversity: 7 genera, 200 species.
Ecology: Largely unknown; nymphs of some Xestocephalus feed on grass roots; Portanini occur in tropical forests.
Diagnosis: Small, usually mottled brown leafhoppers; head produced, rounded, ocelli near anterior margin distant from eyes, lateral frontal sutures extended just ventromesiad of ocelli, antennal ledges well developed; forewing venation complete; hind femur macrosetal formula 2+1+1 (Xestocephalini) or 2+2+1 (Portanini); male plates ligulate; female ovipositor often strongly arcuate.
Similar to: Aphrodinae, Deltocephalinae.


